Description
A business disruption, whether due to natural, accidental or deliberate incidents, can have a major impact on an organization.
Business Continuity Management (BCM) is about identifying the critical business functions that an organization can not afford to lose due to a disruption and planning how to maintain them, if an incident occurs.
With the advent of COVID-19, the importance of setting up a Business Continuity Management System (BCMS) that can effectively handle disruption-related preparation, response and recovery has become well recognized.
Organizations without an effective business continuity measures can lose valuable business to competitors, or even seize to exist all together.
This document covers key BCMS-related best practices and offers general guidance based on the ISO 22301:2019 standard.
Contents
1. Overview
– Context
– Key definitions
– Myth and reality
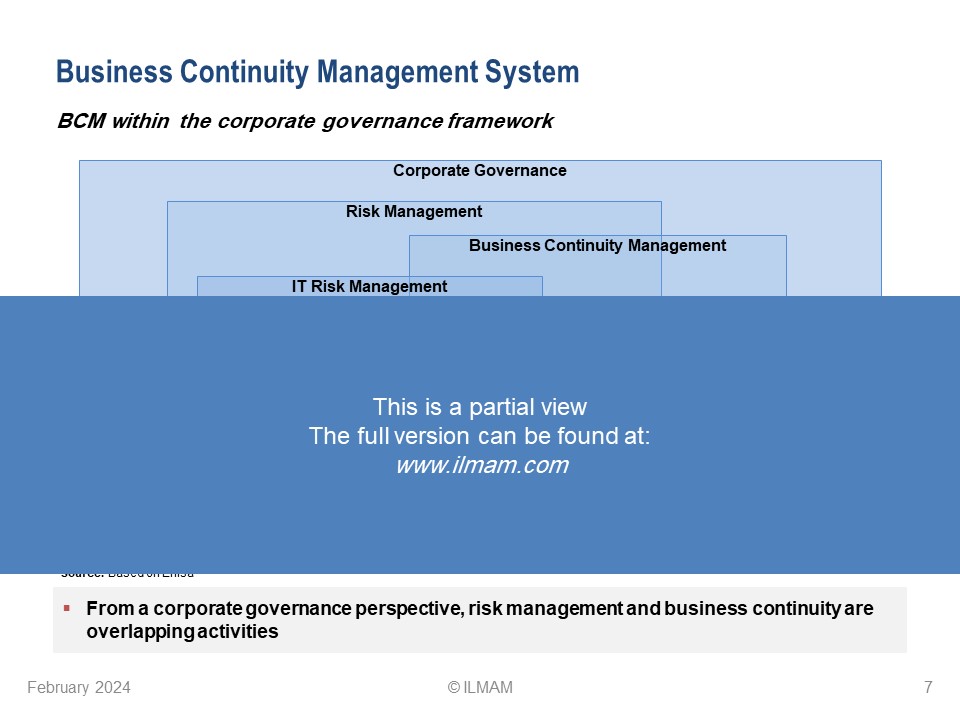
– BCM within the corporate governance framework
– BCMS emphasis
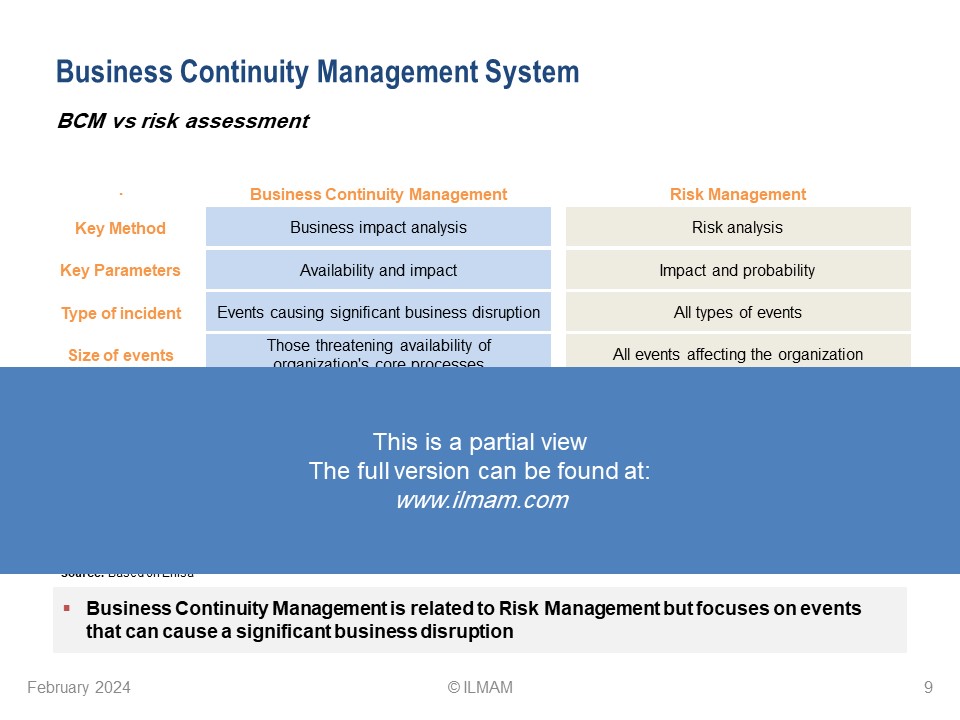
– BCM vs risk assessment
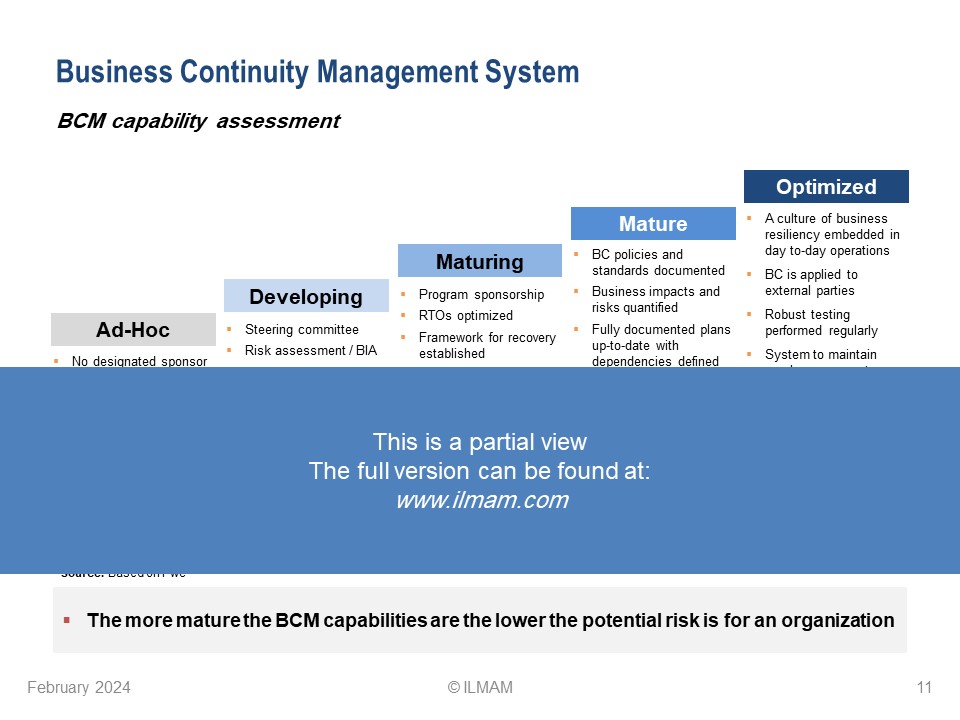
– BCM capability assessment
– BCM maturity assessment
2. Framework
– ISO 22301:2019 History and transition timeline
– ISO 22301:2019 vs ISO 22301:2012
– ISO 22301:2019 – key components
– ISO 22301:2019 and PDCA (plan-do-check-act)
– ISO 22301 and PDCA (plan-do-check-act) ? with descriptions
3. Components
– I. Context of the Organization
– I. Context of the Organization – components
– I. Context of the Organization – Interested parties
– II. Leadership
– III. Planning
– III. Planning – Factors to consider when making changes to the BCMS
– IV. Support
– V. Operation
– VI. Performance evaluation
– VII. Improvement